We all know that recently, the major brands of folding screen cell phones, flexible wearable electronics and other smart devices are emerging. The "era of flexibility" has come, folding screen is one of the hot spots in the cell phone market in recent years, becoming the consensus of the industry. As an important part of flexible electronic devices, flexible sensors are developing from basic research to industrialization.
Sinocrystal would like to share with you the technical knowledge of the raw material -- FPC, to understand how to manufacture FPC and the combination of hard and soft board, which helps us to design the best matching scheme, or provide more angles of analysis ideas in the later anomaly analysis.
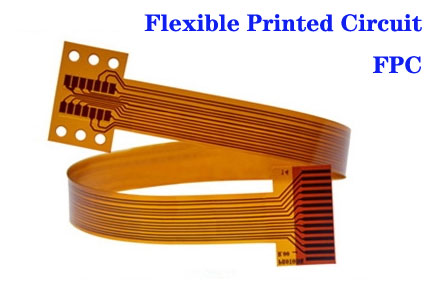
Today we would like to share you of Flexible Printed Circuit materials
1. Substrate and protective layer film
The most common material we use is polyimide (PI), which is so soft and strong that we can't easily tear it or stretch it. It is also incredibly thermally stable and can easily withstand the temperature changes of the reflow process in processing, and we can barely detect its expansion and contraction deformation during the ups and downs of temperature changes.
Polyester (PET) is another commonly used material for flexible circuits, compared with only polyimide (PI) film, which has poorer heat resistance and temperature deformation than PI film. This material is typically used in low-cost electronic devices where printed circuits are wrapped in a flexible film. Since PET cannot withstand high temperatures, let alone solder, the process of cold pressing is generally used to make this flexible circuit board.
I remember that the display part of this clock radio uses this flexible connection circuit, so this radio often does not work properly, and the root cause is this poor quality connection.
So we recommend the flexible and rigid board or choose PI film, other materials are also available but not often used.
PI film, PET film, thin epoxy resin and glass fiber core, are the common materials used for flexible circuits. In addition to that, the circuit needs to use other protective films, usually 23, and sometimes mask solder resist ink is used.
In the same way that a solder layer on a rigid board protects the circuit, the protective film insulates the conductor from the outside world and protects it from corrosion and damage. PI and PET films are available in thicknesses ranging from ⅓ mil to 3 mils, with 1 mil or 2 mil thicknesses being more commonly used.
Glass fiber and epoxy materials are thicker, generally from 2 mils to 4 mils.
2. Conductors
Printed conductors, usually carbon film or silver-based ink, are used in the money-saving electronics mentioned above, but copper conductors are still a common choice.
Depending on the application, we have to choose a different form of copper foil. If the purpose is simply to replace wires and connectors, thus reducing manufacturing time and cost, then electrolytic copper foil, which is well used in stress circuit boards, is the best choice.
3. Adhesives
Often, we need an adhesive to bond the copper foil to the PI film (or other films) because, unlike conventional FR-4 rigid sheets, the surface of the roll-toughened copper foil does not have many burrs, so high temperatures and pressures do not allow for good bonding.
Manufacturers, such as DuPont, offer single- and double-sided, etchable copper-clad laminate films that use an acrylic or epoxy-based adhesive with a thickness of ½ mil or 1 mil, and this adhesive was developed specifically for flexible circuit boards.
"Adhesive-free" laminates are becoming more common due to the introduction of new processes such as coating and depositing copper skins directly on PI films. Such films can be useful in HDI circuits that require finer pitches and smaller vias.
Silicone, hot melt or epoxy resins are used when protective beads are added to the hard and soft bond. This enhances the mechanical strength of the hard and soft bond and ensures that no stress fatigue or tearing occurs during repeated use.
All in One: It is important to have a clear understanding of the materials used in flexible or rigid-flexible circuit boards.
We are free to choose materials according to the application, but this sets up the end product for failure.
Understanding the properties of materials can also help us to design, evaluate and test the mechanical part of the product.
If the product being developed is for an automotive application, heat dissipation, moisture resistance, chemical corrosion, and impact all need to be carefully simulated so that the correct material is used to achieve high product reliability and a minimum allowable bend radius.
在数字时代,LCD屏幕无处不在,从手机和平板电脑到电视和显示器。尽管LCD技术已经相当成熟,提供了成本效益高且性能稳定的显示解决方案,但在其生命周期中,用户可能会遇到各种显示问题。本文深入探讨LCD显示屏的常见不良现象,分析其原因,并提供针对性的解决方案,帮助用户和技术人员更好地理解和维护他们的设备。
TFT-LCD屏可视为两片玻璃基板中间夹着一层液晶,上层的玻璃基板是与彩色滤光片(ColorFilter)、而下层的玻璃则有晶体管镶嵌于上。当电流通过晶体管产生电场变化,造成液晶分子偏转,藉以改变光线的偏极性,再利用偏光片决定像素(Pixel)的明暗状态。此外,上层玻璃因与彩色滤光片贴合,形成每个像素(Pixel)各包含红蓝绿三颜色,这些发出红蓝绿色彩的像素便构成了皮肤上的图像画面。
在精密电子产品的物流运输中,包装不仅是产品的“外衣”,更是品质的“护城河”。尤其是对于显示屏这类易碎且对环境要求极高的产品,包装的科学与严谨直接关系到最终交付的完好率。
市面上最常见的触摸屏按结构划分,主要分为电阻式触摸屏和电容式触摸屏两大类。它们各自拥有独特的工作原理和特性,适用于不同的场景。我们将客观地从核心原理、外观显示、用户体验、耐用性及应用场景等多个维度,为您深入剖析电阻屏与电容屏的区别,助您为产品选择最合适的交互方案。
产品开发时怎么判断选择定制显示屏还是标准现货?本文分析如何选择适合我们产品项目的显示屏,真正做到节省成本的显示屏采购方案。
每款产品的功能都不一样,显示需求也有差异,往往需要定制显示屏。在以往的经验种我们得知很多客户因为不熟悉显示屏定制的流程,导致反复“试错”花费大量的沟通成本和时间成本。本文详细拆解显示屏定制流程,帮助工程和采购更好地对接显示屏厂推进项目落地。